Information Communication and Technology
Moving from Primary to Secondary
We develop from the KS3 curriculum with three core strands following the national curriculum; Digital Literacy, ICT and Computer Science.
Creating Subject Experts
Helping our learners become great experts in ICT.
Our aim in KS3 is to develop students core skills in digital literacy, computer science and ICT.
We have developed a spiral curriculum to support students build on key skills such as programming. We aim to provide a supporting and nurturing atmosphere and develop independent learners across the key strands.
KS3 - Develop students for a breadth of specialisation at KS4 with a key focus on sparking students interest by keeping lessons relevant and sharing a bigger picture.
KS4 - Here students begin to specialise in subjects such as computer science where it is key to develop independent problem solving skills.
KS5 - Our ICT curriculum at KS5 is still accessible for students who have not taken computer science at KS4 and with a vocational focus helps prepare them for the real world of work.
Subject Disciplines (Skills)
Computer Science
- Design, use and evaluate computational abstractions that model the state and behaviour of real-world problems and physical systems
- Use 2 or more programming languages, at least one of which is textual, to solve a variety of computational problems; make appropriate use of data structures [for example, lists, tables or arrays]; design and develop modular programs that use procedures or functions
ICT & Digital Literacy
- Undertake creative projects that involve selecting, using, and combining multiple applications, preferably across a range of devices, to achieve challenging goals, including collecting and analysing data and meeting the needs of known users
Create, reuse, revise and repurpose digital artefacts for a given audience, with attention to trustworthiness, design and usability
Subject Substantives (Knowledge)
Computer Science
- Understand several key algorithms that reflect computational thinking [for example, ones for sorting and searching]; use logical reasoning to compare the utility of alternative algorithms for the same problem
- Understand simple Boolean logic [for example, AND, OR and NOT] and some of its uses in circuits and programming; understand how numbers can be represented in binary, and be able to carry out simple operations on binary numbers [for example, binary addition, and conversion between binary and decimal]
- Understand the hardware and software components that make up computer systems, and how they communicate with one another and with other systems
- Understand how instructions are stored and executed within a computer system; understand how data of various types (including text, sounds and pictures) can be represented and manipulated digitally, in the form of binary digits
ICT & Digital Literacy
- Understand a range of ways to use technology safely, respectfully, responsibly and securely, including protecting their online identity and privacy; recognise inappropriate content, contact and conduct, and know how to report concerns
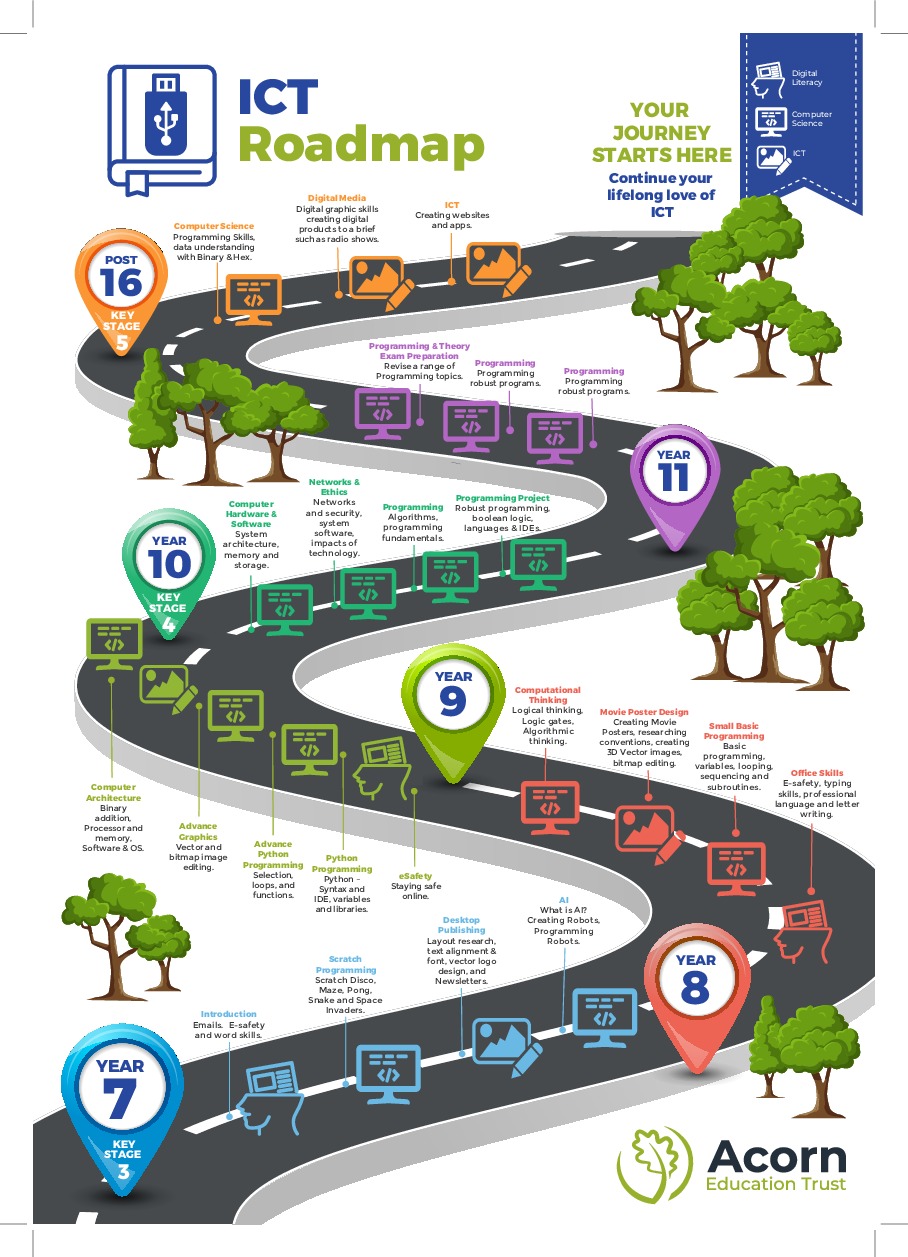
Roadmap
How we assess your child
Assessment Grades KS3
Students complete assessments in each of their subjects at key points during the year which test their understanding of all the knowledge they have learnt to date (we call these cumulative assessments). We grade these assessments on a scale from 1-9 (9 being the highest). The assessments are designed so that each year they become more challenging and test students on their growing bank of knowledge.
Therefore, as an example, if your child achieves a grade 5 in an assessment in Year 7, we can predict confidently that they should go on and achieve at least a grade 5 at GCSE. This is providing they keep working hard and progressing. Please note: this prediction states “at least”. Students often achieve higher than this.
In years 7 – 9, in practical subjects (PE, Drama, Music etc.), we assess students on their practical ability and skills. This gives us a strong indication of how successful they would be if they chose one of these subjects as a GCSE option. However, in order to get a fuller view of their potential success, it is also important to consider their grades in the core subjects. This is because there is often a literacy, numeracy, or scientific element to the courses.
Assessment Grades in KS4
Students complete mock exams in each of their subjects at key points during the year which test their understanding of all the knowledge they have learnt to date. We grade these mock exams on a scale from 1-9 (9 being the highest). In the report you will see:-
- Target Grade: This is based on a student’s past performance. It is an aspirational but achievable target
- Mock Grade: The grade they achieved in the mock exam
- Predicted Grade: The grade a teacher believes a student will achieve in the final exam, if they maintain their current ATL and performance
Assessment Grades in KS5
Students complete mock exams in each of their subjects at key points during the year which test their understanding of all the knowledge they have learnt to date. We grade these mock exams on a scale from A*-E/Distinction* - Pass. In the report you will see:-
- Target Grade: This is based on a student’s past performance. It is an aspirational but achievable target
- Mock Grade: The grade they achieved in the mock exam
- Predicted Grade: The grade a teacher believes a student will achieve in the final exam, if they maintain their current ATL and performance
Exam Board Information
Computer Science – OCR GCSE Graded 1-9 (Two exams at the end of year 11 both worth 50% of the final grade)
Creative iMedia – OCR Cambridge Nationals Level 1/2 (One Exam at the end of year 11 worth 40% and two coursework based pieces worth 25% and 35% wach)



